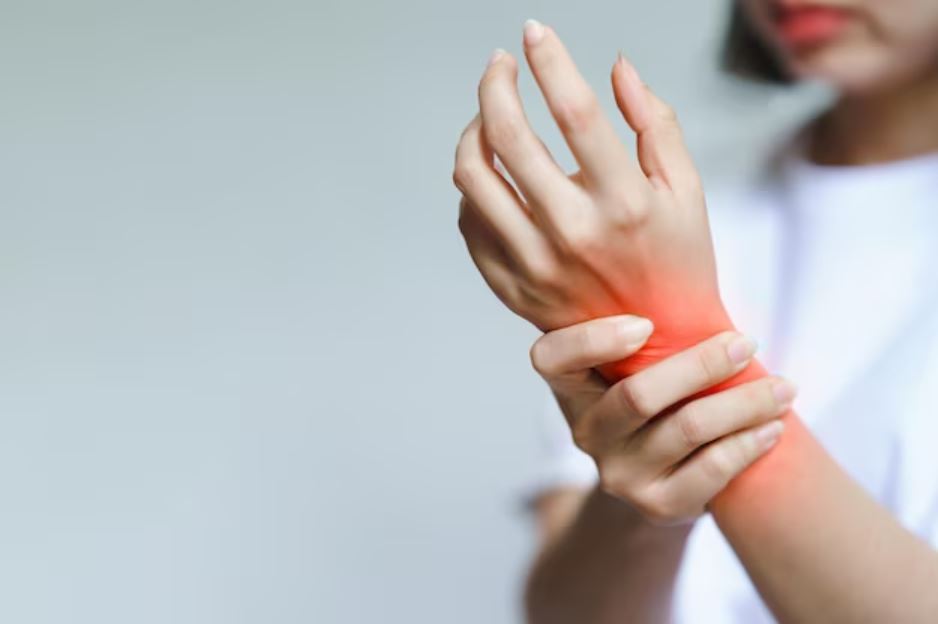
The hallmark of rheumatoid arthritis (RA), a chronic inflammatory disease, is joint inflammation. Millions of people are impacted globally, and it results in pain, stiffness, and decreased mobility. It is essential to comprehend the origins, signs, diagnosis, and available treatments for RA in order to manage the illness and enhance quality of life.
Introduction to Rheumatoid Arthritis
The joints are the main organs affected by the systemic inflammatory disease rheumatoid arthritis. The synovium, the lining that lines joints, becomes inflamed when the immune system unintentionally targets the body’s own tissues. Over time, the damage to bone, cartilage, and other joint tissues caused by this chronic inflammation can result in pain, swelling, and stiffness.
Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Although the precise origin of rheumatoid arthritis is unclear, a mix of environmental and genetic factors is thought to be responsible. In addition to environmental factors including smoking, infections, and hormone fluctuations, some genetic markers can raise the chance of having RA. An aberrant immune system reaction results in long-term inflammation and joint degeneration.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis symptoms might differ from person to person, but they usually include stiffness, swelling, and discomfort in the joints, especially in the mornings or after periods of inactivity. There might be other symptoms include weakness, fever, exhaustion, and weight loss. Numerous joints in the body, including the hands, wrists, knees, ankles, and feet, can be impacted by RA.
Diagnosis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
A combination of medical history, physical examination, blood testing, and imaging investigations is usually used to diagnose rheumatoid arthritis. The diagnosis can be supported by the presence of certain antibodies in the blood, such as rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies. To evaluate joint injury, imaging tests including MRIs, ultrasounds, and X-rays may also be performed.
Treatment Options
Rheumatoid arthritis has no known cure, but there are a number of therapy choices that can help control symptoms, delay the illness’s development, and enhance quality of life. Pain and inflammation can be lessened with the use of medications such as biologic agents, disease-modifying antirheumatic medications, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs). To increase joint function and mobility, recommendations may also be made for physical therapy, exercise, and assistive technology.
Managing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Managing rheumatoid arthritis requires coping mechanisms and good lifestyle choices in addition to medication. Symptoms can be reduced with the use of pain management strategies such heat and cold treatment, relaxation methods, and stress reduction. For general well-being, getting adequate sleep, eating a balanced diet, and exercising frequently are crucial.
Complications of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis can cause major side effects, such as joint abnormalities, loss of function, and disability, if it is not treated or managed properly. Sometimes, RA can impact the heart, lungs, eyes, and other organs and systems in the body, resulting in further health issues. Appropriate treatment and early diagnosis are essential for avoiding or reducing these consequences.
Prevention Strategies
Rheumatoid arthritis cannot be completely prevented, but some lifestyle modifications and proactive steps can lower the chance of getting it or help treat its symptoms more successfully. Joint health may be supported by abstaining from smoking, keeping a healthy weight, and taking precautions to prevent joint injuries. Regular monitoring and early intervention can also have an impact on how a condition is managed.
Nutritional Considerations
The management of rheumatoid arthritis is greatly influenced by nutrition, as specific foods and dietary habits can either increase or decrease inflammation. Reduced inflammation and symptom relief can be achieved with an anti-inflammatory diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean meats, and healthy fats. Flaxseeds and fish oil, which are rich sources of omega-3 fatty acids, may also have anti-inflammatory properties.
Alternative Therapies
Certain individuals with rheumatoid arthritis may find relief from complementary and alternative therapies including massage therapy, acupuncture, and herbal medicines in addition to standard medical treatments. When combined with conventional treatments, these therapies may provide further pain relief and enhance general well-being, while further study is required to validate their efficacy.
Research and Future Directions
New information and possible treatment approaches are always being discovered by ongoing research into the mechanics and causes of rheumatoid arthritis. Future developments in immunology, genetics, and biotechnology may lead to more specialized and individualized RA treatment strategies. In order to improve outcomes for RA patients, new medicines and interventions are being tested in clinical trials.
Coping with Rheumatoid Arthritis
It can be difficult to manage rheumatoid arthritis on both a physical and psychological level. It’s critical that people with RA learn coping mechanisms and enlist the help of friends, family, and medical professionals. Participating in counseling or therapy, joining support groups, and learning relaxation methods can all help lessen the condition’s related tension, anxiety, and sadness.
Impact on Daily Life
Relationships, employment, and everyday activities can all be significantly impacted by rheumatoid arthritis. Both productivity and quality of life may be impacted by pain, fatigue, and mobility issues. The impact of RA on day-to-day living can be reduced by implementing accommodations at home and at work, utilizing mobility aids and assistive technology, and maintaining open lines of communication with loved ones and employers.
FAQ's
Users often search for information on the initial symptoms of RA to identify the condition early. Providing insights into early signs like joint pain, stiffness, and swelling can help individuals recognize potential RA symptoms sooner.
This question reflects a common concern among individuals diagnosed with RA or those experiencing symptoms. Users seek clarity on whether there’s a definitive cure for the condition or if treatment focuses solely on symptom management and disease control.
People frequently search for information on effective treatment strategies for managing RA symptoms. Addressing this FAQ by outlining various treatment options such as medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies can provide valuable guidance.
Prevention is a key aspect of healthcare, and users often inquire about preventive measures for rheumatoid arthritis. Providing insights into risk factors, lifestyle modifications, and early intervention strategies can help individuals understand how to reduce their risk of developing RA or mitigate its impact.
Nutrition plays a significant role in managing rheumatoid arthritis, and users commonly search for dietary recommendations. Addressing this FAQ by highlighting foods that may exacerbate inflammation or trigger RA symptoms can help individuals make informed choices about their diet and lifestyle.